Finding deleted and changed webpages
There are many guides to using the Google search engine and there's no need to repeat it all here. However, the following features are useful to anyone trying to gather evidence for a complaint.
Browser add-ons for searching cached pages
Search engine website caches
As search engines trawl through the Internet, they creates snapshot copies of the pages they finds — these copies are called cached pages. If a website owner removes or changes the content of a page on their website, the cached copy will be deleted or updated the next time the search engine checks it. This means that, even though a page may have changed or been deleted, it may still be available in the search engine's cache. How long it remains there depends on how frequently the search engine checks that website: popular websites and pages may be checked very frequently, but for less popular ones, the old cached page may remain there for days or weeks.
This means that, even though a page has been changed, it may be possible to see what it said before that change. This can be very useful in researching.
Access to these cached Google pages is easy and can be done in several ways.
Search results
When Google returns the results of a search, it usually has a link to the cached page — click on the small down arrow to the right of the website's url and click on 'Cached':
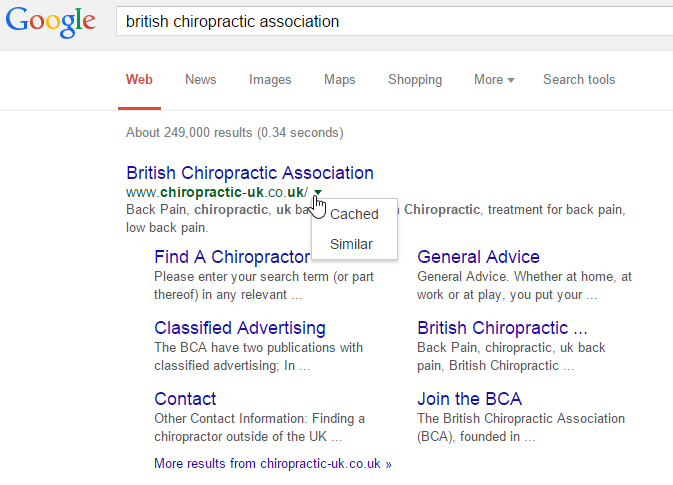
This will give you Google's cached version of the website's home page.
However, if you want to look at a different page and already know its URL, you can look at the Google cached page by entering the following into the Google search box in your browser (Chrome and Firefox) or in the Google search box:
![]()
Cache results
At the top of the returned page, Google gives information about the cached page. For example:

This gives the date and time Google cached the page, which could be useful to help determine whan a page changed. It also gives a link to the current page.
A useful feature of the cached page is that any search terms you used will be highlighted on the page, making it much quicker, especially in a text heavy page, to see how frequently your search terms appear and in what context.
Other Google functions
Google has other useful functions related to this. If you enter info: followed by a URL, you will see something like this:

Of these, the fourth one is very useful. This allows you to see all pages that Google has found on that website. You can get to this directly by entering site: followed by the URL into Google's search box. If you add a search term as well, Google will return a list of the pages on that website that have that word in them. This is Google's Site Search and is useful particularly if the website does not offer its own search facility and it will frequently return more results.
For example, if you enter:
site:www.chiropractic-uk.co.uk "simon singh"
…you will see all pages on the BCA's website that mention Simon Singh. Currently, there are none.
A feature of Google's Site Search is that it will return pages even if they are not currently accessible from a link on another page, but which were linked to when Google indexed the site. This is particularly useful in finding pages that have been 'removed' but are still, in fact, on the website and can still be returned by search engines.
Because a page is in Google's cache, it can appear in the search results, bringing a viewer to their website, even though it is disconnected from the rest of the web site.
If you can't remember the exact URL you can search for a word within the URL using inurl: and add a search term to refine things, eg inurl:nightingale skeptics and site:URL filetype:pdf would let you uncover .pdfs within a given site's URL. There are many other search refinements in the 'Advanced search' option — see Further reading, below.
Wayback machine
This is the Internet's Tardis. The Wayback Machine is on archive.org and it caches a large number of webpages and allows you to look at them on different dates (unlike the search engine caches that only retain the page the last time it crawled it). Note that it doesn not capture every change made, but it can be very useful for finding content at some previous time.
Browser add-ons for finding cached pages
If you use Firefox you can download the 'Resurrect Pages' add-on gives easy access to a number of caches, including Google's and the Wayback Machine. For Google's Chrome browser, try the Web Cache extension.
Further reading
![]() Finding things that aren't there any more on the internet, and storing things that are
Finding things that aren't there any more on the internet, and storing things that are
Latest news
- "Undisputable evidence of scientific misconduct" by homeopaths
- Yet another bad year for homeopathy
- Nelsons Homeopathic Pharmacy #3
- Nelsons Homeopathic Pharmacy #2
- The Society of Homeopaths: failing to make the case for homeopathy
- The end of homeopathy on the NHS in Bristol?
- NHS Homeopathy: 20 years of decline
- The different faces of the Society of Homeopaths
- The growing pains of osteopaths
- Diluting misleading claims - ASA update
Most read
- Finding deleted and changed webpages
- About The Nightingale Collaboration
- How to find out who owns a website
- Advertising Standards Authority
- Rubbing salts into the wounds of homeopathy
- How to submit a complaint to the ASA
- The decline of homeopathy on the NHS
- Landmark decisions for homeopaths
- NHS Lanarkshire to end referrals to Glasgow Homeopathic Hospital
- Making a complaint

